Besrt Describes Best Gas Law Molar Mass
Where m is the mass of the gas and M is the molar mass. Note also that both sides of the Ideal Gas Law equation have the dimension of energy J kg m 2 s 2.

Gas Law Problems Combined Ideal Density Molar Mass Mole Fraction Partial Pressure Effusion Youtube
The molar mass form of the ideal gas equation can be written as.

. Since we know that 6022 1023 represents Avogadros number and is the. Equation 21 is a form of the ideal gas law. Now if a fixed mass of gas undergoes an expansion at constant temperature then the final volume and pressure shall be p 2 and V 2.
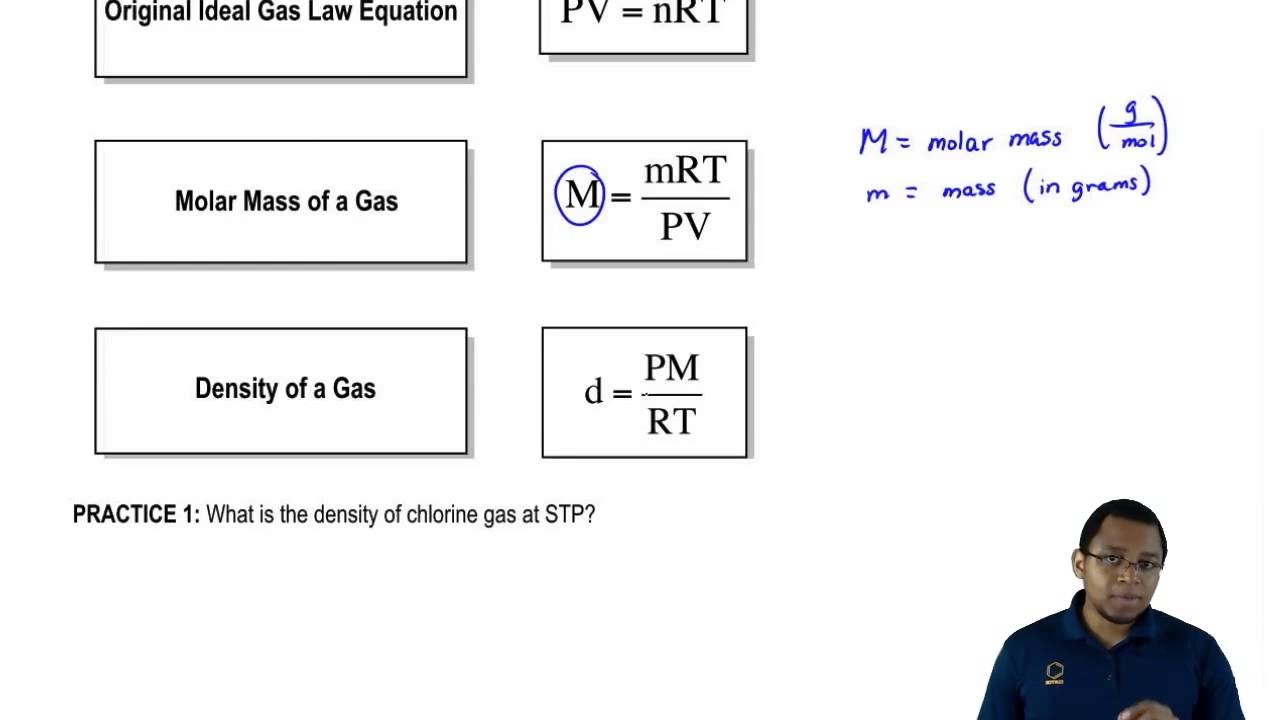
There are several relationships between the temperature pressure the number of moles and the volume of gases. N m M n m M. PV mM RT.
The molar mass of a gas can be derived from the ideal gas law P V nRT by using the definition of molar mass to replace n the number of moles. Charles law says at constant pressure the volume and temperature of a sample of gas. V is the volume of that container.
A 1525g mass of a volatile liquid is vaporized giving 500 mL of vapor when measured over water at 30C and 770 torr. Sep 24 2005 1 Canuck156. Questions refer to three gases in identical rigid containers under the conditions given in the table below.
The simplicity of this relationship is a big reason why we typically treat gases as ideal unless there is a good reason to do otherwise. P V RT m M P V R T m M. K 1 pV.
A 11 B 12 C 21 D 13. The Ideal Gas Law can be further manipulated into new equations. R is the ideal gas constant 8314 Joules per mole-Kelvin.
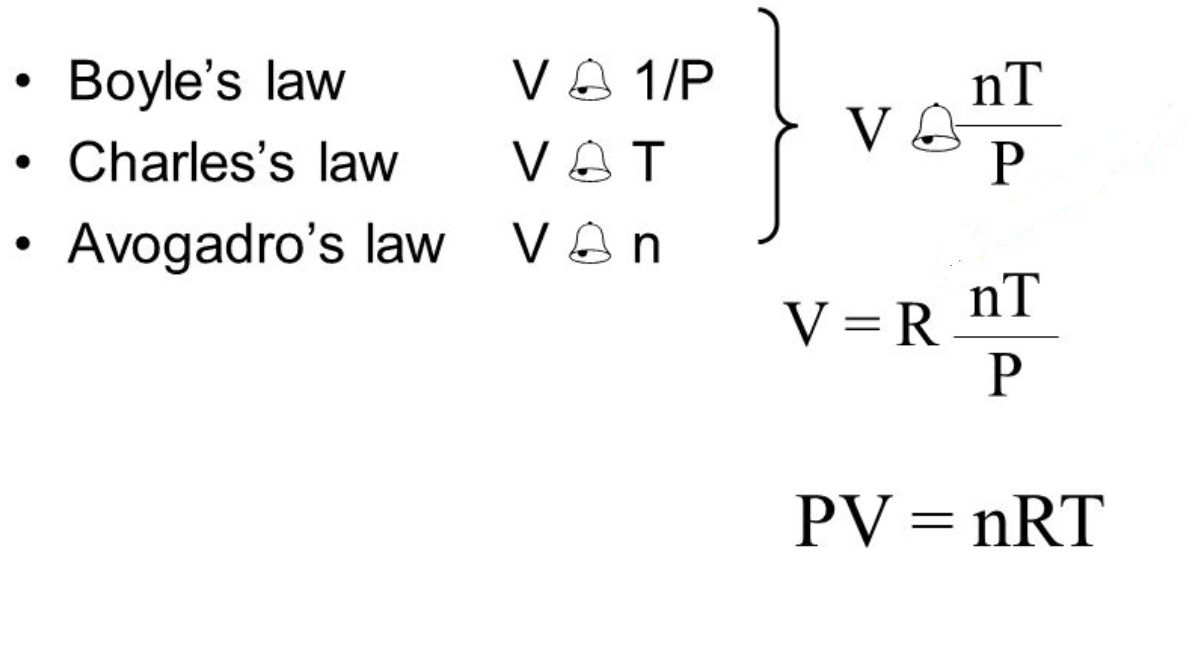
Boyles law says at constant temperature the volume and pressure of a sample of gas are inversely proportional V 1P. Our gas law calculator uses the following equations. We can write n number of moles as follows.
The molar mass of an ideal gas can be determined using yet another derivation of the Ideal Gas Law. Recall that a mole is 602 x 10 23 molecules Avogadros Number. At 27C 240g of a certain gas occupies a volume of 984 L at a pressure of 172 torr.
Mass not required for number of moles calculations. For a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to its volume. Watch more of this.
The molecular masses of the gases because the gas molecules have the same average kinetic energy and mass can be calculated using the equation KEavg12mv2KEavg12mv2. LatexnfracmMlatex where m is the mass of the gas and M is the molar mass. P V m MRT P V m M R T.
The vapor pressure of water at 30C is 32 torr. Hi this is the question Im having trouble with. Besrt Describes Best Gas Law Molar Mass.
Ideal Gas LawMolar Mass Thread starter Canuck156. Finally putting the equation in terms of molar mass we have. You are holding two balloons an orange balloon and a blue balloon.
The ideal gas law best describes the properties of which of the following gases at 0C and 1 atm. Molar mass is defined as the mass of a substance occupied by exactly 6022 1023 of that respective gas atoms or molecules. As you study chemistry you need to get comfortable working with a unit of measurement called the mole.
Start date Sep 24 2005. The Ideal Gas Law Molar Mass and Density. P is the pressure the gas exerts on the walls of the container that confines it.
Moles Pressure Volume 00821 Temperature If you want to work it out yourself without the molar mass of gas calculator be careful with the units. Calculate the molar mass of the gas. The orange balloon is filled with neon Ne gas and the blue balloon is filled with argon Ar gas.
The ideal gas law best describes the properties of which of the following gases at 0C and 1 atm. The mixture has a density of 147gL at 100 atm and 298K. Calculating Molar Mass using the Ideal Gas Equation.
The modified ideal gas law formula. If the molar volume of a gas at STP is 224 litres how many moles are there in 112 litres of hydrogen gas. Volume of the gas ml L dm³ m³.
We can plug this into the Ideal Gas Equation. The orange balloon has twice the volume of the blue balloon. A single mole tells us the number of atoms found in 12 grams of carbon-12.
Where p is pressure Pa kg m 1 s 2 V is the volume m 3 N is the number of moles R is the gas constant 8314 J K 1 mole 1 and T is the temperature K. Which one of the following statements best describes Boyles Law. What happens to the path of.
Or P ρM RT as described below. Multiplication of the left and right sides of Equation ref1051 by the molar mass in gmol M of the gas gives rho dfracgLdfracPMRT label1052 This allows us to determine the density of a gas when we know the molar mass or vice versa. What Are Moles.
Which of the following best represents the mass ratio of NeAr in the balloons. Which of the following best helps explain why the pressure of a sample of CH 4g molar mass 16gmol. According to ideal gas law PVnRT n massmolar mass PV mMRT ----- PM mVRT ----- PM dRT Including compressibility factor Z we get PM ZdRT at 473K and 1 atm Z PMdRT 1atm18gmmol 0804gmL View the full answer.
These new equations can help us find the density or molar mass of a gas. The pressure volume and temperature of an ideal gas are related by a simple formula called the ideal gas law. We can plug this into the Ideal Gas Equation.
The initial volume and initial pressure here is p 1 and V 1 then according to Boyles law. A gas mixture is known to contain equal numbers of moles of two gases. On rearranging we get.
Density mw x P RT Soif P R and T are the same the gas with the greatest molar mass will have the greatest density. Where is the pressure of the gas is the volume taken up by the gas is the temperature of. T is the temperature of the gas.
CH 4 is 22400 cm 3 and its molar mass is 16 grams then how many grams of methane are there in 112 cm 3 of methane gas. Density of a gas is generally expressed in gL mass over volume. In a diffusion experiment one of the gases was found to.

Ideal Gas Law Overview Calculations Expii
Using The Ideal Gas Law To Find Density Or Molar Mass Youtube
No comments for "Besrt Describes Best Gas Law Molar Mass"
Post a Comment